Exercise linked to enhanced brain function in adults at risk for Alzheimer’s Disease
Regular aerobic exercise may decrease the likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease, or slow its progression, in adults who are at a higher risk, according to a new study from the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health (UW SMPH).

Stem cells could help cancer patients fight dangerous infections
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have developed a more efficient way to grow the white blood cells, which serve as front-line defenders against bacterial infections but are often depleted as a potentially deadly side effect of cancer treatment.

UW–Madison study shows that calorie restriction slows skeletal muscle aging
Monkeys on calorie restricted diets age better than monkeys on a normal diet, according to researchers at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health.

Scoring system predicts seizure risk in hospitalized patients
A new rating system can accurately predict which critically ill patients are in danger of having seizures while hospitalized, a large, multi-national trial shows.

Survey of the Health of Wisconsin now an ICTR-CAP affiliate program
This November, the Survey of the Health of Wisconsin (SHOW) joined the Institute for Clinical and Translational Research’s Community-Academic Partnership program as an affiliate member.

Access to Medicare increases cancer detection, reduces cancer mortality rate
Access to Medicare significantly impacts detection of certain cancers and life expectancy following cancer diagnosis, according to a new study from the UW School of Medicine and Public Health that was recently published online in the Journal of Policy Analysis and Management.

UW–Madison inventors aim to replace old-style breast-surgery marker
Three University of Wisconsin–Madison innovators have invented a better way for surgeons to locate tumors during lumpectomies for breast cancer.
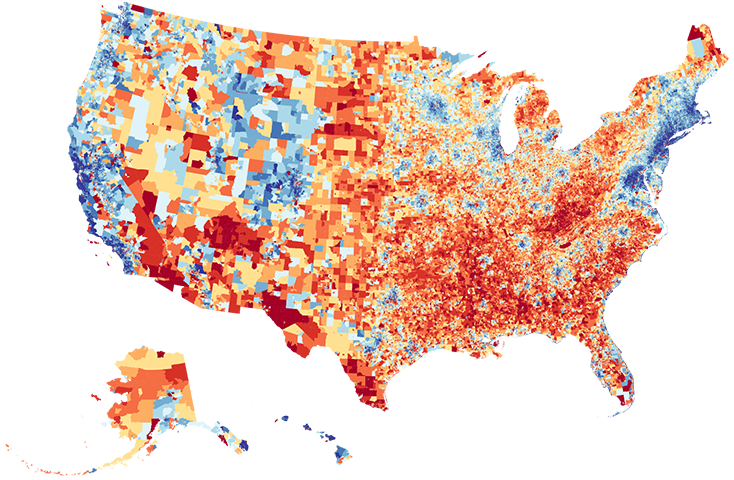
UW–Madison study finds where you live affects brain health
Living in disadvantaged neighborhoods may impact the brain, according to researchers at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health.

Inflammation predicts response to anti-depression medication
Children and teens with bipolar depression responded better to an antipsychotic medicine if they had increased markers of inflammation in their blood, a new University of Wisconsin–Madison study shows.

Low genetic risk for ADHD may protect against negative life experiences
A recent study shows that people at low genetic risk for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are not only less likely to have the disorder, they also have better than expected economic, health and behavioral outcomes in later life.
New tool predicts three-dimensional organization of human chromosomes
University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers have developed a computational tool that can accurately predict the three-dimensional interactions between regions of human chromosomes.

Delirium linked to brain injury after severe surgery
Researchers at the UW School of Medicine and Public Health discovered that delirium following severe surgery may be associated with brain injury.