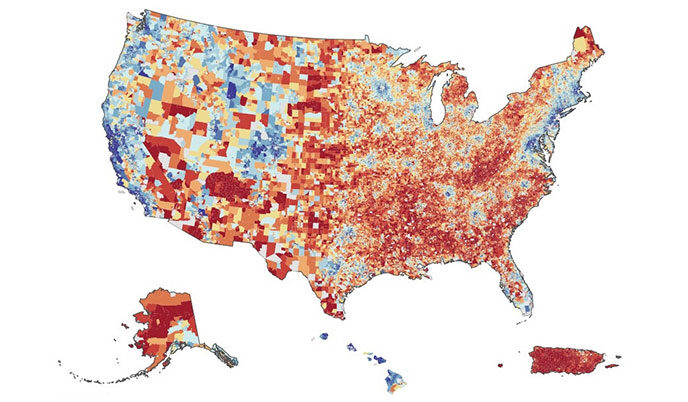
Federal agency uses UW–Madison Neighborhood Atlas research to shape national health policy
A data tool developed by UW–Madison researchers showing health-relevant metrics for every neighborhood in the United States is guiding a national model to help Medicare beneficiaries from under-resourced communities access health care more effectively.

Affordable Care Act slashed uninsured rate among people with diabetes
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provided health insurance for an estimated 1.9 million people with diabetes, according to a newly published study.

New Osher Center for Integrative Health launches at UW–Madison
After more than a year of planning and development, the University of Wisconsin Integrative Health program officially opened the Osher Center for Integrative Health at University of Wisconsin‒Madison.

Lupus much more likely to cause cardiovascular problems in Black patients
A population-based study of the autoimmune disease lupus in Black patients shows that the risk of cardiovascular disease is strikingly high in young patients –19 times higher than in non-Blacks in the first 12 years after diagnosis – and may be predicted by a characteristic rash.
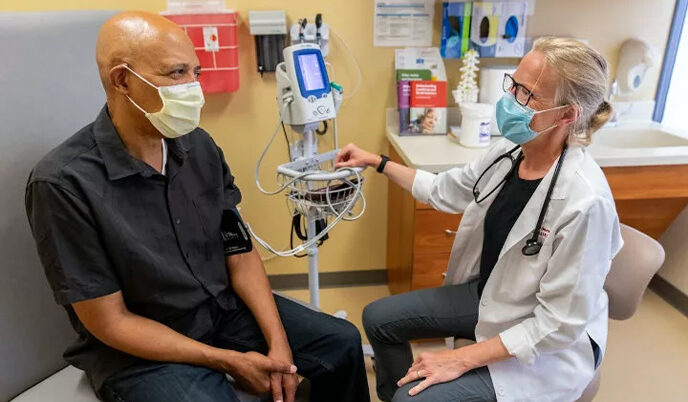
UW study focuses on Alzheimer’s disease treatment and prevention in Black adults
As the first of a new generation of Alzheimer’s disease drugs hit the market, some researchers are troubled by the lack of clinical data available on the effectiveness of these drugs in Black people.

College wrestlers who rapidly cut weight more prone to injury
Collegiate wrestlers who cut weight through dehydration to compete at a lower weight class were more likely to be injured during competition and no more likely to win, according to a new study from the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health.
Antibody treatment reduces asthma attacks in children living in disadvantaged urban areas
A monoclonal antibody drug called mepolizumab decreased asthma attacks by 27% in children and adolescents who have a form of severe asthma, are prone to asthma attacks and live in low-income urban neighborhoods, according to a clinical trial sponsored and co-funded by the National Institutes of Health. The majority of the trial’s participants were Black and/or Hispanic—populations that have been under-represented in clinical trials and are at greatest risk for morbidity and mortality from asthma.

Researchers identify ways to improve emergency care for people living with dementia
A new collection of research papers sets out priority areas to better provide emergency care for people living with dementia in the United States.

‘C’ for Wisconsin on Population Health Report Card
New study: Longer is better when treating opioid addiction with medication
A large study of Medicaid patients found that the longer they take medication to treat their opioid use disorder, the less likely they are to overdose.

UW Study: Most teens actually have healthy relationship with digital technology
Parents play a major role in whether teens’ use of digital technology is healthy or puts their mental and physical health at risk, according to a new study from the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health.

Rural patients who identify as Black experience higher rates of death and amputation from diabetic foot ulcer
Rural patients who identify as Black are at sharply increased risk of death or leg amputation due to diabetic foot ulcers, according to a new study from the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health that analyzed national data on patient outcomes.