
Cancer research conference focuses on targeted radionuclide therapy
University of Wisconsin-Madison is hosting a national conference on targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT), a promising new technology that combines cytotoxic radioisotopes with molecularly targeted agents to produce an anti-cancer therapy capable of treating local or systemic disease.

‘Clamp’ regulates message transfer between mammal neurons
A fundamental question in nerve biology brings to mind a race car at the starting line: The engine is revving, but the brake is on. The system is ready to go, but under tight control.

Electronic records pin broad set of health risks on genetic premutation
It was long believed the FMR1 premutation — an excessive number of trinucleotide repeats in the FMR1 gene — had no direct effect on the people who carry it. Until recently, the only recognized effect on the carriers of the flawed gene was the risk of having offspring with fragile X syndrome, a rare but serious form of developmental disability.

Changing a single molecule in the brain can alleviate anxiety
A new study shows, for the first time in primates, that altering one particular molecule in a specific brain region can change “dispositional anxiety,” the tendency to perceive many situations as threatening. The finding provides hope for new strategies focused on intervening early in life to treat people at risk for anxiety disorders, depression, and related substance abuse.

Single protein plays important dual shipping role in the brain
Just as a packaging breakdown can hamstring delivery of cables, switches and connectors to a house under construction, removing a protein from neurons can block the “shipment” of proteins to developing axons.

Study finds major surgery is associated with minor cognitive decline
A new study by researchers at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health has revealed that major surgery is associated with only a minor decline in cognitive ability.

UW launches nation’s first cell therapy trial for kidney transplant patients
For the first time in the United States, a research team will test a personalized cell therapy to treat a common and serious complication facing kidney transplant patients.

Lessons of conventional imaging let scientists see around corners
Along with flying and invisibility, high on the list of every child’s aspirational superpowers is the ability to see through or around walls or other visual obstacles.

Study: Wisconsin rule limiting full-contact practice in high school football cuts concussion rate by more than half
The rate of sport-related concussions during high school football practice in Wisconsin decreased by 57 percent following a rule change limiting the amount and duration of full-contact activities during practice, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health.

Simultaneous infection by two viruses the key to studying rare lymphoma
New research has found that a rare blood cancer can be simulated in the lab only by simultaneously infecting white blood cells with two viruses typically found in the tumors.
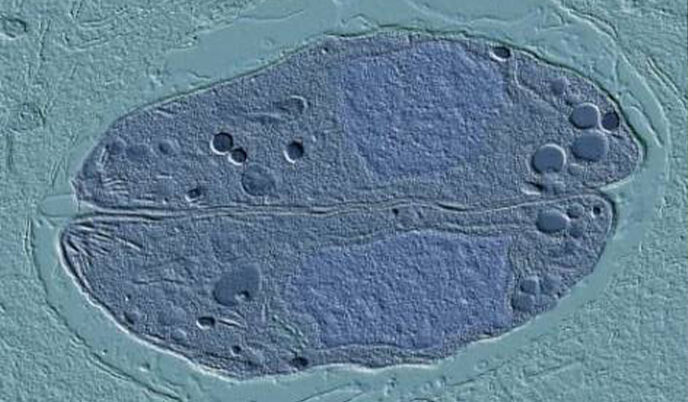
Thanks to science, parasite can have sex in mice, not just cats
Toxoplasma gondii, a single-celled parasite perhaps best known for its ability to trick mice into taking potentially fatal risks around cats and, in humans, as a serious threat to fetal health, has given up a long-held secret of its reproduction.

Can a sleep device give deep-space explorers a good night’s rest?
The Wisconsin Institute for Sleep and Consciousness (WISC) will be one of two sites for testing a device that might improve sleep and thus waking performance for people on long space voyages.