
UW shows strong presence at Alzheimer’s Association International Conference
The world’s largest and most prestigious Alzheimer’s disease conference is underway this week, and UW Alzheimer’s disease researchers are attending in high numbers, leading several important discussions.

UW begins new clinical trial to treat fatal blood diseases in children, young adults
A clinical trial has launched at the UW School of Medicine and Public Health to test the safety of a new type of stem cell transplantation to treat a variety of deadly blood disorders in children and young adults.

Patient with rare cancer uses telehealth to access clinical trial
Today is National Clinical Trials Day, and UW Health wants to celebrate the researchers, nurses, physicians and experts in the lab who make clinical trials available and impactful for our patients and community. UW Health officials also say virtual consultations have been vital to expanding access to clinical trials for Wisconsin residents, especially during the pandemic.

UW to lead national research on pediatric asthma in low-income urban areas
The UW School of Medicine and Public Health has been selected as the national leadership center for a new clinical research network that will conduct pediatric asthma research in low-income urban settings around the country.
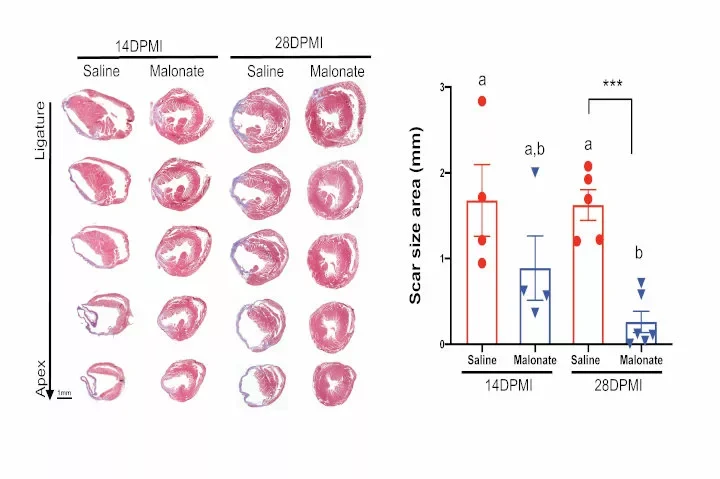
Metabolic switch may regenerate heart muscle following heart attack
New research from the University of Wisconsin–Madison finds that a new therapeutic approach for heart failure could help restore cardiac function by regenerating heart muscle.
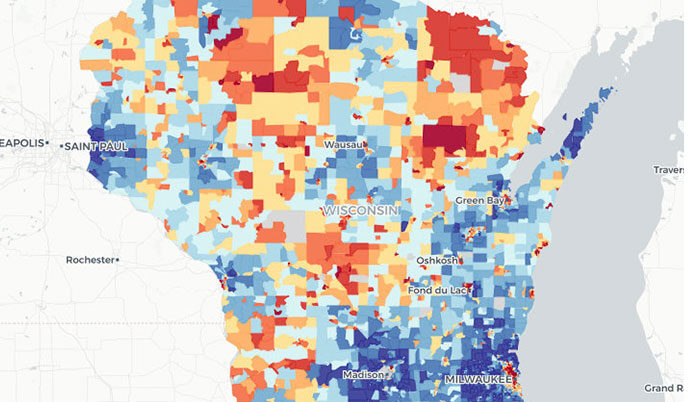
Alzheimer’s study finds link between living in disadvantaged neighborhoods and brain shrinkage, declining brain function
In a newly published study, researchers at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health report finding a correlation between living in neighborhoods with the fewest social and economic advantages and experiencing changes in brain structure and function that are characteristic of Alzheimer’s diseases and related dementias.

New UW study examines immune response to COVID-19 vaccine in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
A new study at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health is looking at the immune response to COVID-19 vaccines in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Enrollment is open now for patients who fit the criteria.
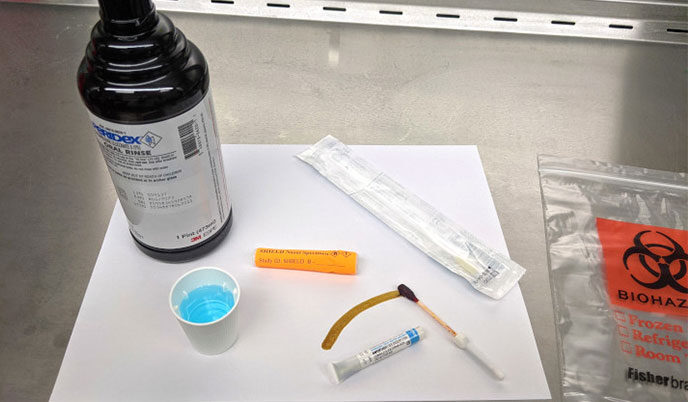

UW COVID-19 prevention study expands enrollment to essential workers
All essential workers who cannot perform work duties remotely are now eligible to take part in a prevention research study at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. The study is investigating whether commonly used oral and nasal antiseptic, in addition to masks and hand hygiene, can help prevent COVID-19 infections. These workers include police officers, firefighters, daycare workers, grocery store workers, retail employees, restaurant staff, mail carriers and bus drivers, etc.

Study finds analyzing DNA in urine could help detect cancer
A study published this week in Science Translational Medicine describes how urinalysis could potentially be used to detect some forms of cancer.

All of Us Research Program returns first genetic results to participants
Participants who donated biosamples, as part of the historic “All of Us” Research Program, may soon see a return of their genetic results.
UW researchers develop tool to equitably distribute limited vaccines
The demand for COVID-19 vaccines continues to outpace supply, forcing public health officials to decide who should be first in line for a shot, even among those in the same pool of eligible vaccine recipients.
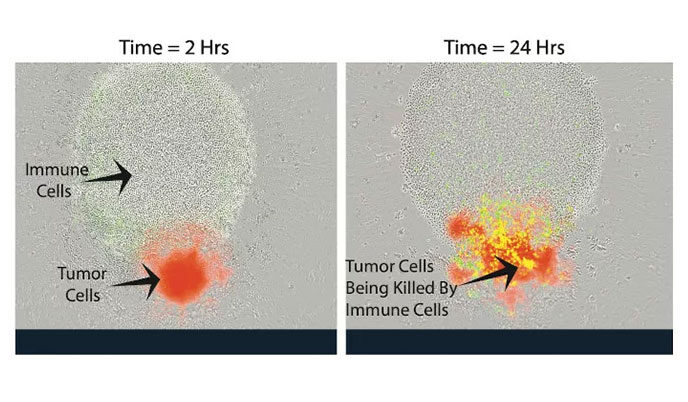
Jamey Weichert, Zachary Morris leading a team to develop new way to help immune system fight back against cancer
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health are breaking new ground to make cancer cells more susceptible to attack by the body’s own immune system.